Differential Pressure Regulators
What are differential pressure regulators? What do they do? Let’s take a look and find out.
The important point to understand with differential pressure regulators is that there are two loading pressures acting on the diaphragm. The first loading pressure is the outside or reference signal. This can come from air, liquid or steam. The second loading pressure is the downstream pressure. The differential between the reference pressure and the downstream pressure is determined by the spring, referred to as the differential force.
Differential regulators will maintain the downstream pressure at a set level between the reference pressure. Hence, the spring range determines the differential pressure and it can be changed by increasing or decreasing the tension on the spring.
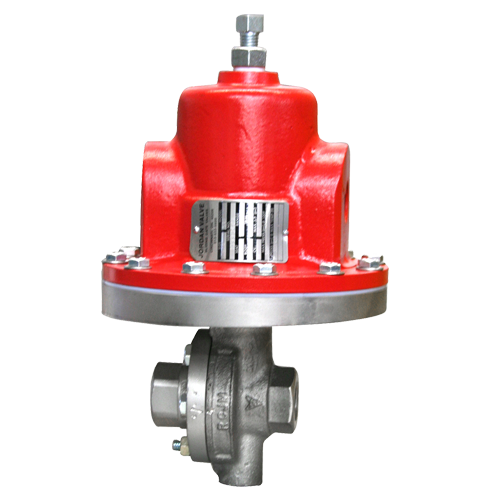
Mark 64 Differential Regulator with Flow through Dome
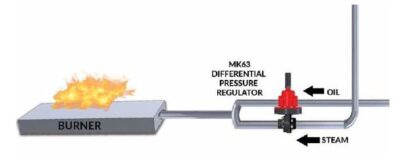
Above is the schematic of the Mark 63 Differential/Atomizing valve. The fuel oil is our reference pressure and it enters the regulator through the top dome area while the steam is carried in the main line through the valve body. The valve is used to maintain steam pressure at a constant differential above the oil pressure. This assures effective atomization of the fuel oil into droplets (mist), so a flame can be produced and a clean burn achieved.

