Steam Tracing for Pipe Protection
Mark 86 AmbiTemp regulator for worry-free control of steam trace lines
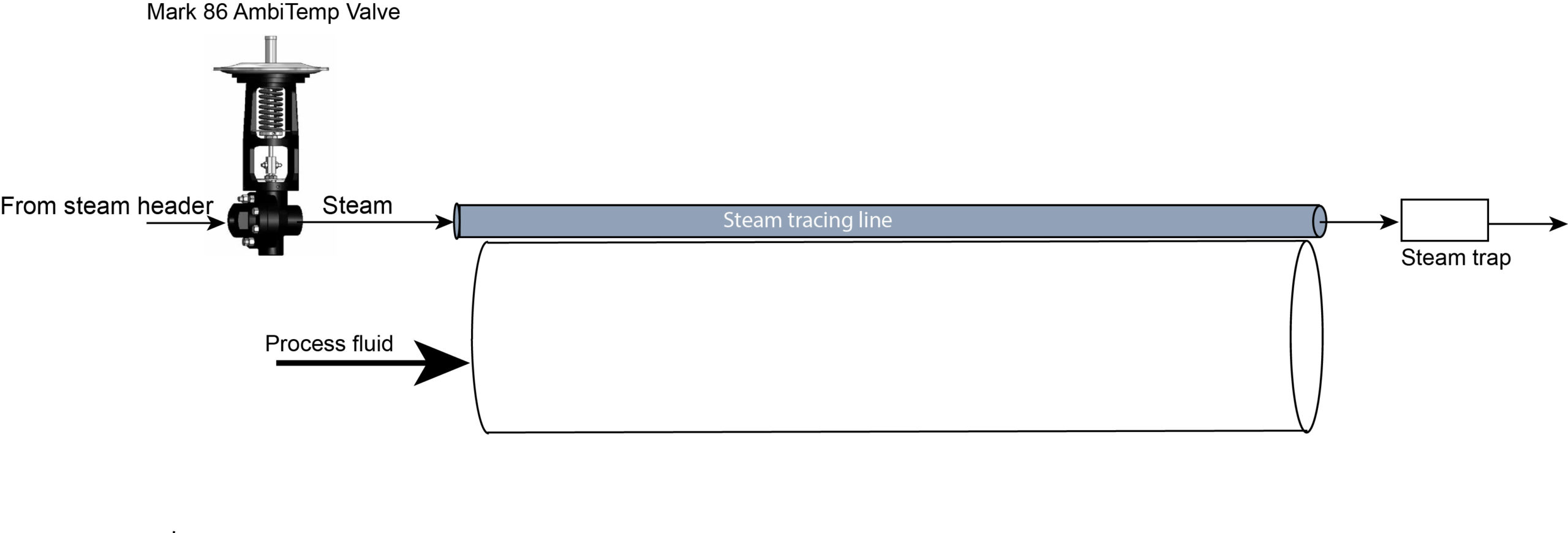
What is steam tracing?
Steam tracing is a heating method used for pipelines to maintain process fluids at a specified elevated temperature. It is a type of heat tracing for process lines transporting media that are adversely affected by cold conditions or temperature dips. Heat tracing methods include fluid heating and electric heating. In steam tracing, small diameter tubes, called trace lines, are installed in direct contact with process pipelines and carry steam controlled to a certain temperature setpoint. Steam temperature is easy to control because it has a fixed relationship to steam pressure and is an efficient heat carrier.
When to use steam tracing
Steam tracing is used in industries such as chemicals production and oil refineries where process fluids are transferred through outdoor pipelines with regularly changing ambient temperatures. Heat tracing or steam tracing is particularly important in these conditions. Common reasons to use steam tracing include:
- Protect product from freezing
- Maintain product viscosity
- Avoid chemical separation
- Prevent solidification or crystallization
- Avoid gas condensation
Ambient Temperature Steam Tracing
Ambient temperature is ever changing throughout the seasons and when the temperature drops, it is time to turn the steam tracing system on so products don’t freeze, separate or become compromised due to low temperatures. Conversely when the temperature rises, it’s time to turn the steam tracing off. Remembering when to open the steam tracing system or turn the steam off for seasonal temperature fluctuation is a test of the memory. One forgetful moment could have big implications. Jordan valve has an Ambient Temperature steam tracing valve that avoids having to remember seasonal on/off dates for steam tracing.
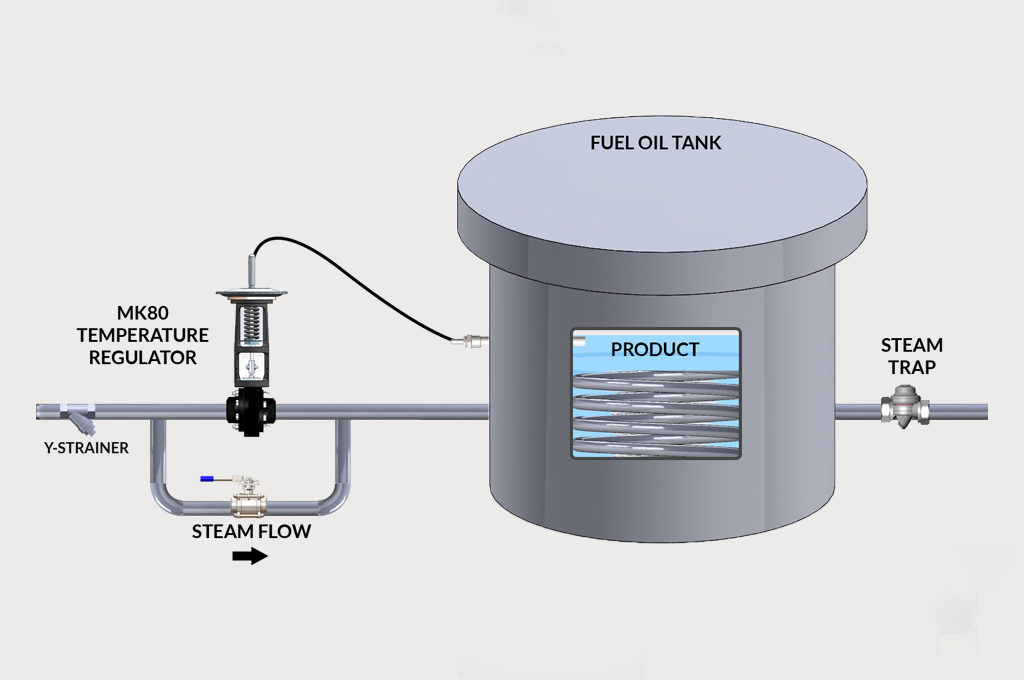
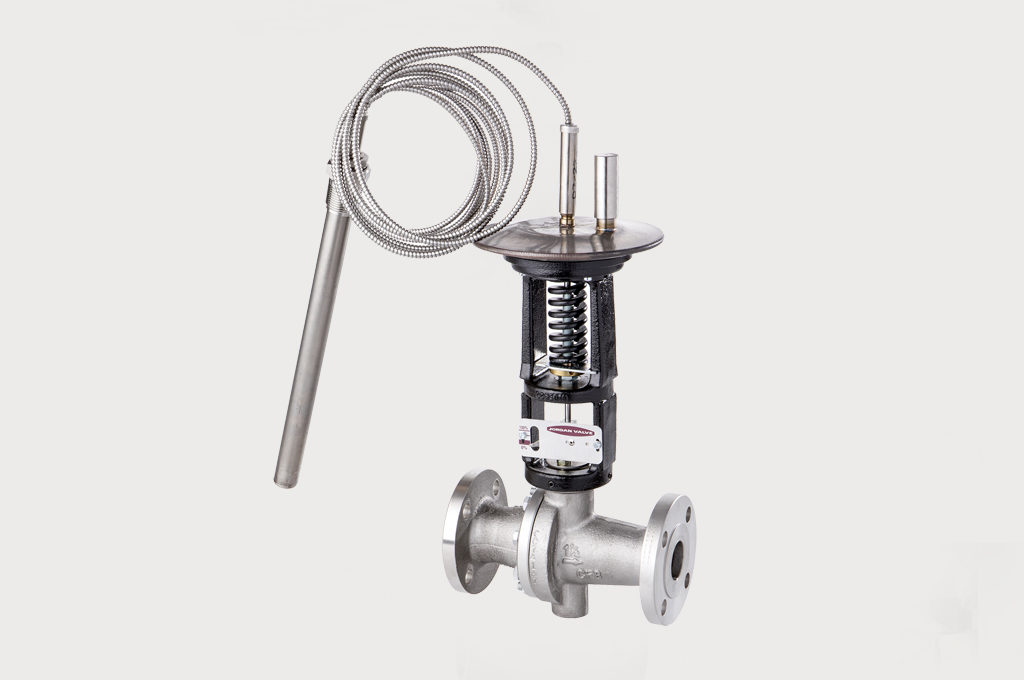
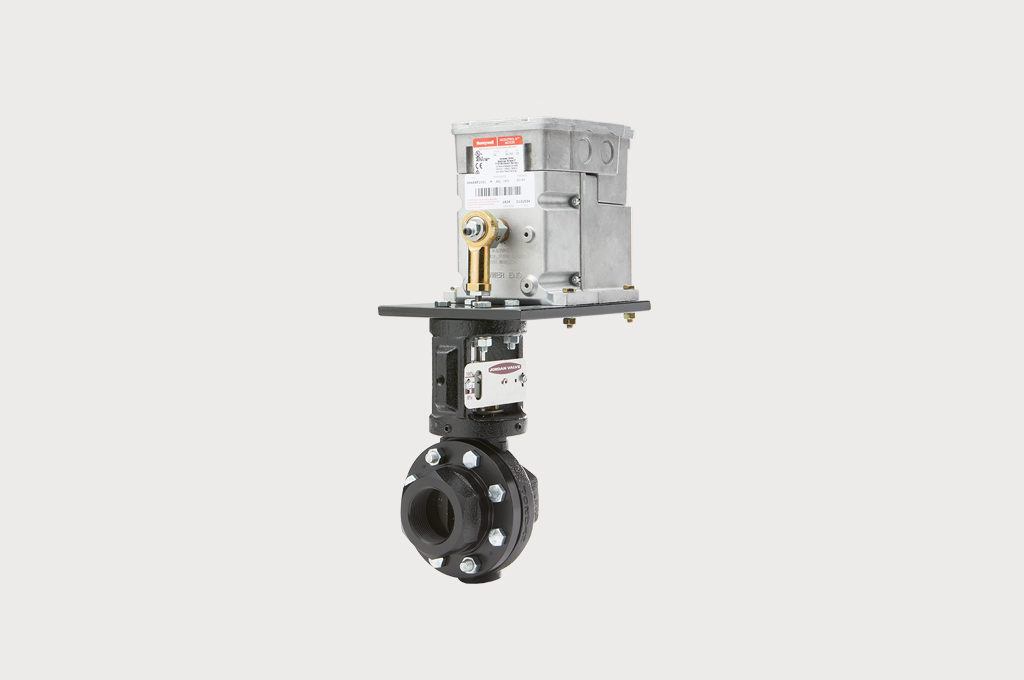
Mark 86 Ambient Temperature Regulator
The Mark 86 “AmbiTemp” regulator is a self-actuating regulator designed to open and close based on ambient temperatures. It allows steam to flow through tracing lines only when it is needed, saving operational costs. The Mark 86 regulator opens to allow steam into the trace lines when ambient temperature drops below desired setpoint and closes trace lines when temperatures rise above setpoint. Because it is self-actuating, the valve cycles without the need for electricity, air or operator intervention.

For example, to avoid freezing a product with a freezing point of 38°F, the temperature on the Mark 86 can be set to actuate at 45°F, comfortably above freezing point. As the ambient temperature falls below the set point, the valve will automatically open, allowing steam to enter the tracing system. Once the ambient temperature rises above the set point, the valve will close and conserve the steam.
The operation of the MK86 is fairly simple. A pre-measured amount of liquid fill is drawn into the thermal system filling the upper diaphragm chamber. As the ambient temperature increases, the volatile liquid in the sensing chamber begins to vaporize and creates pressure on the sealed system. This pressure drives the valve stem, closing direct acting valves. It is installed as a normally closed valve.
The Mark 86 requires no capillary or sensing bulb. The actuator on the Mark 86 serves as both sensing element and the power element.
The Mark 86 is designed using the unique Jordan sliding gate technology for superior response, wide range of Cvs and increased service life. They are available with several temperature ranges and line sizes. Contact us for more information.
Let us help you find the right valve for your application.
Related Resources
How Temperature Regulators and Control Valves Work
Using Self-Operated Temperature Regulators to Control Steam

Steam Temperature Control of Jacketed Tanks
Steam pressure control is vital for maintaining consistent tank jacket temperature

Steam Curing Cinder Blocks
Accurate steam control for precision autoclave dryer performance
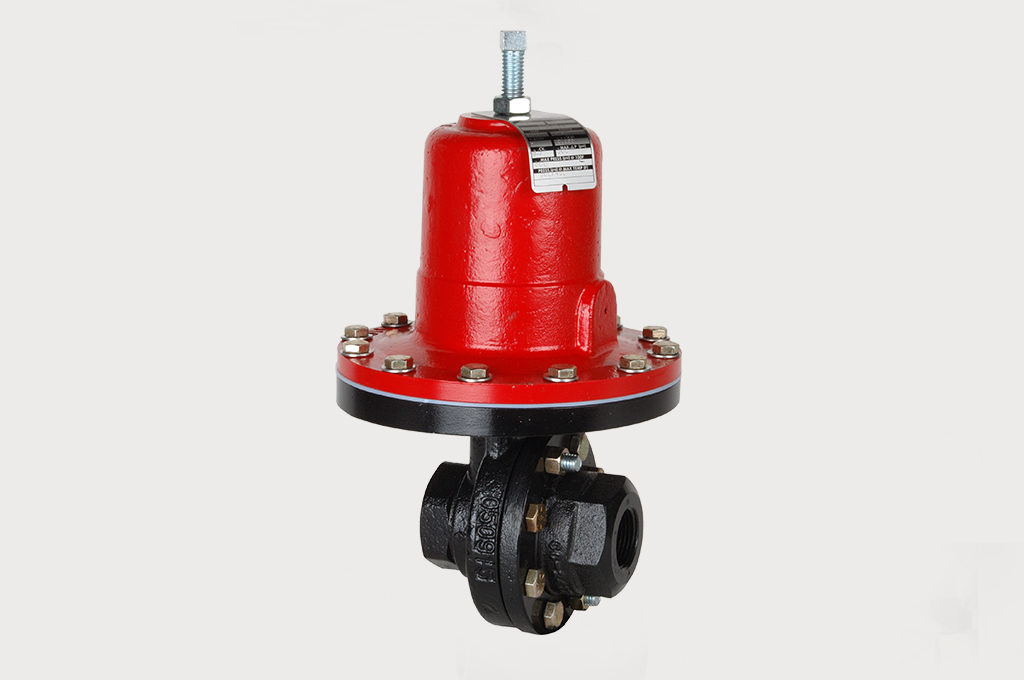

Steam Sterilization
Jordan Valve sliding gate valves with Jorlon® diaphragms outlast in challenging steam sterilizing process
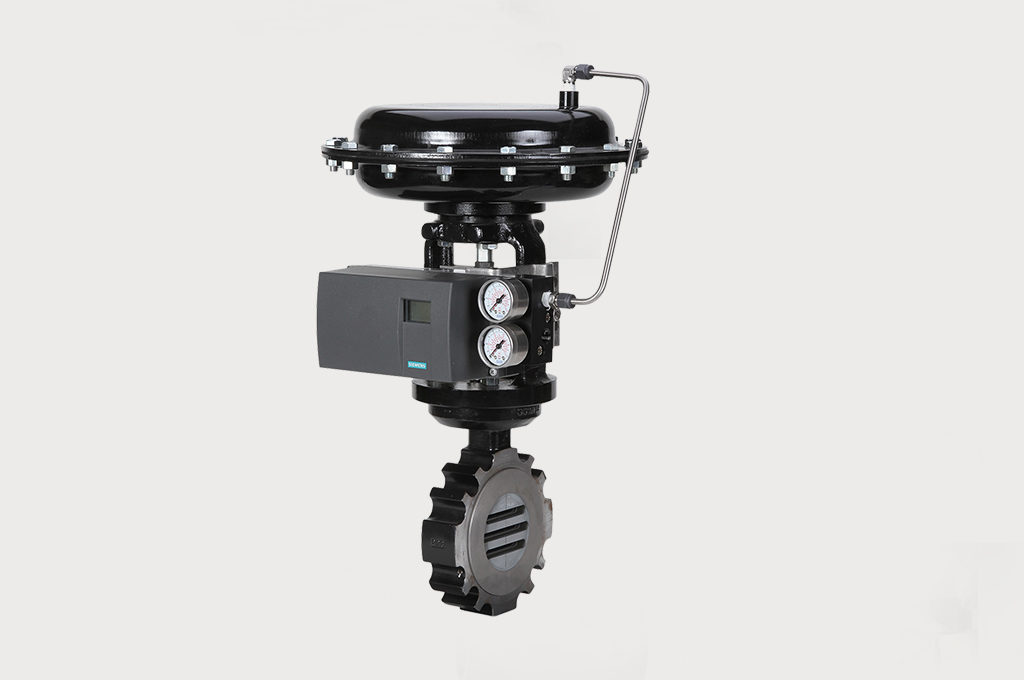

Precision Steam Control
Jordan Sliding Gate Valve for Precise, Efficient Steam Control
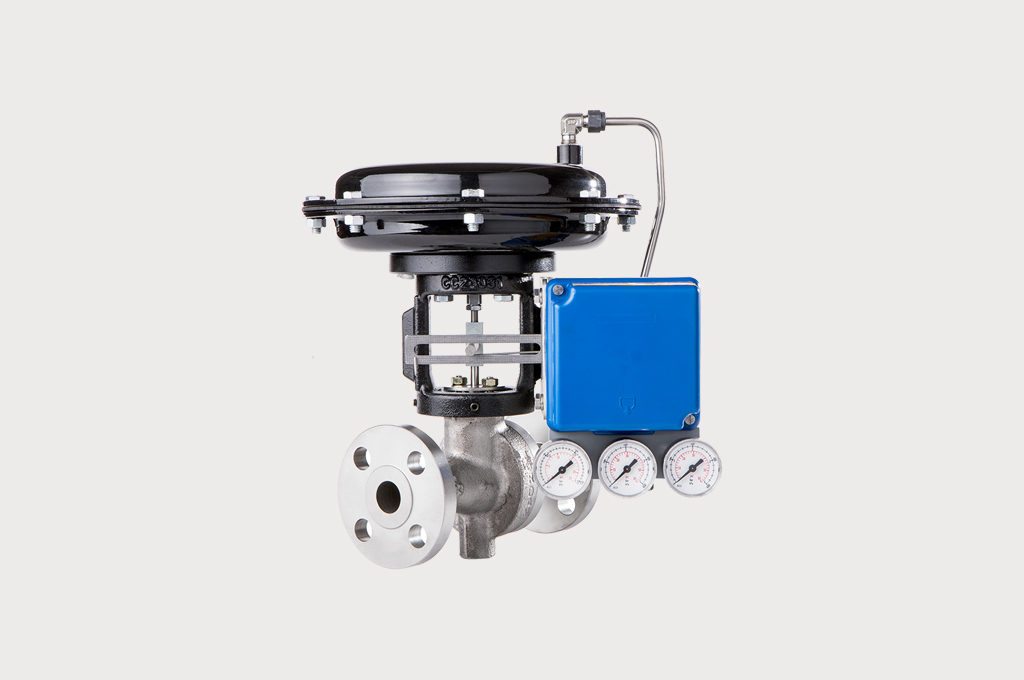

Steam Valve for Tire Curing Press
Jordan Valve sliding gate technology outperforms in challenging tire curing process
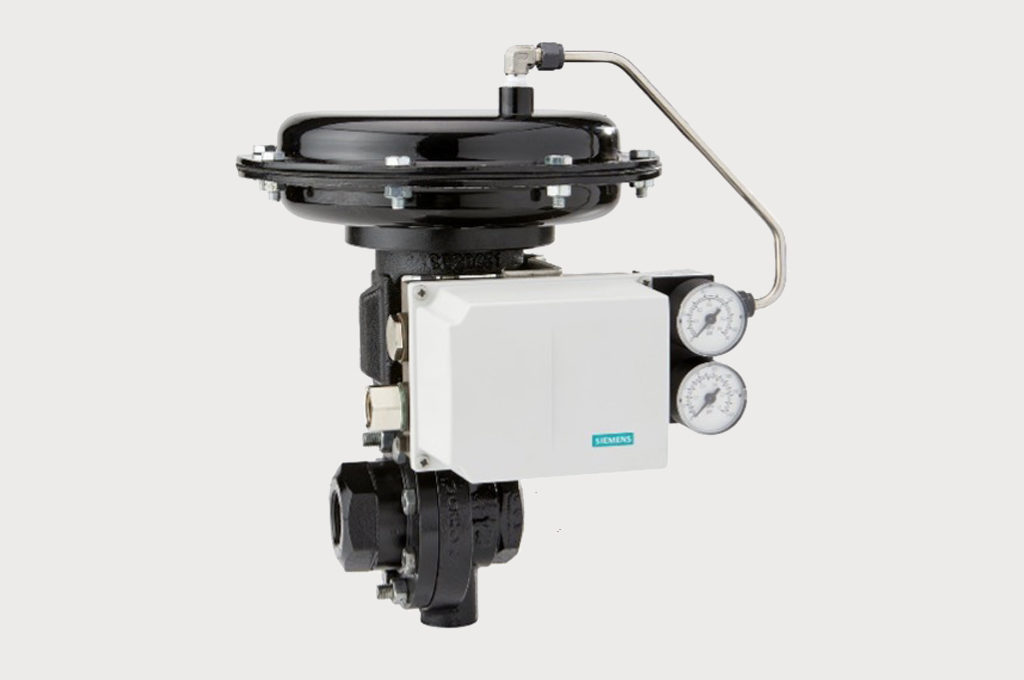

Better Steam Pressure Control Improves Drying for Coating Process
Jordan Mark 701 Sliding Gate Control Valves give Tighter Temperature Control, Faster Throughput

Boiler Feedwater Control
Jordan Mark 33 feedwater control valve maintains accurate level in boiler steam drum.

 Mark 86 Series Ambient Temperature Regulator
Mark 86 Series Ambient Temperature Regulator